Product Search
Solution Search
Searchable by product name, product model or standard.
*To search by solution, switch to “solution search.”
i.e., Load Cells, ZTA-50N, 7864 (for ISO 7864)
Searchable by you force type, industry, standard or product sample.
*To search by product, switch to “product search.”
i.e., Compression, 7864 (for ISO 7864)
SEARCH

Torque
- Force Measurement IMADA
- SOLUTIONS
- Torque
Torque
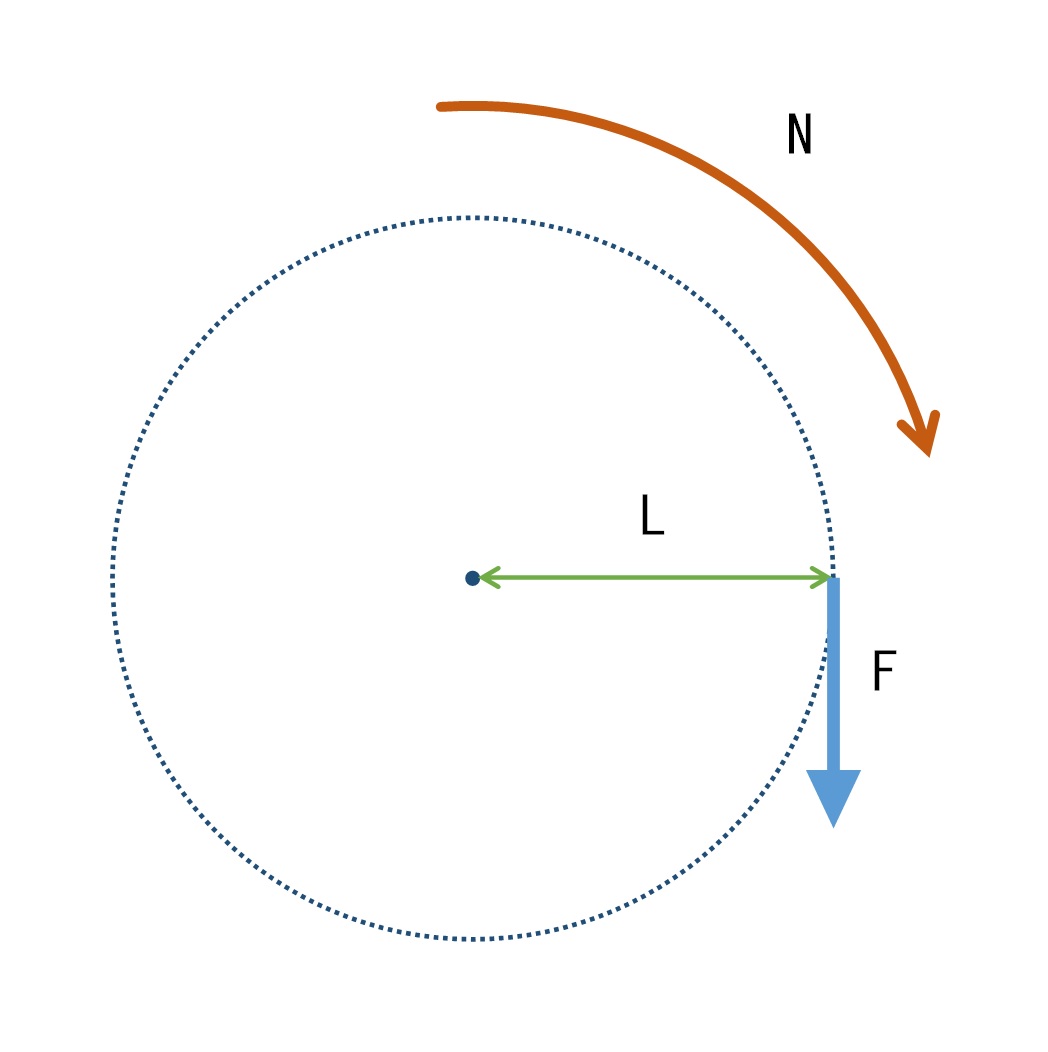
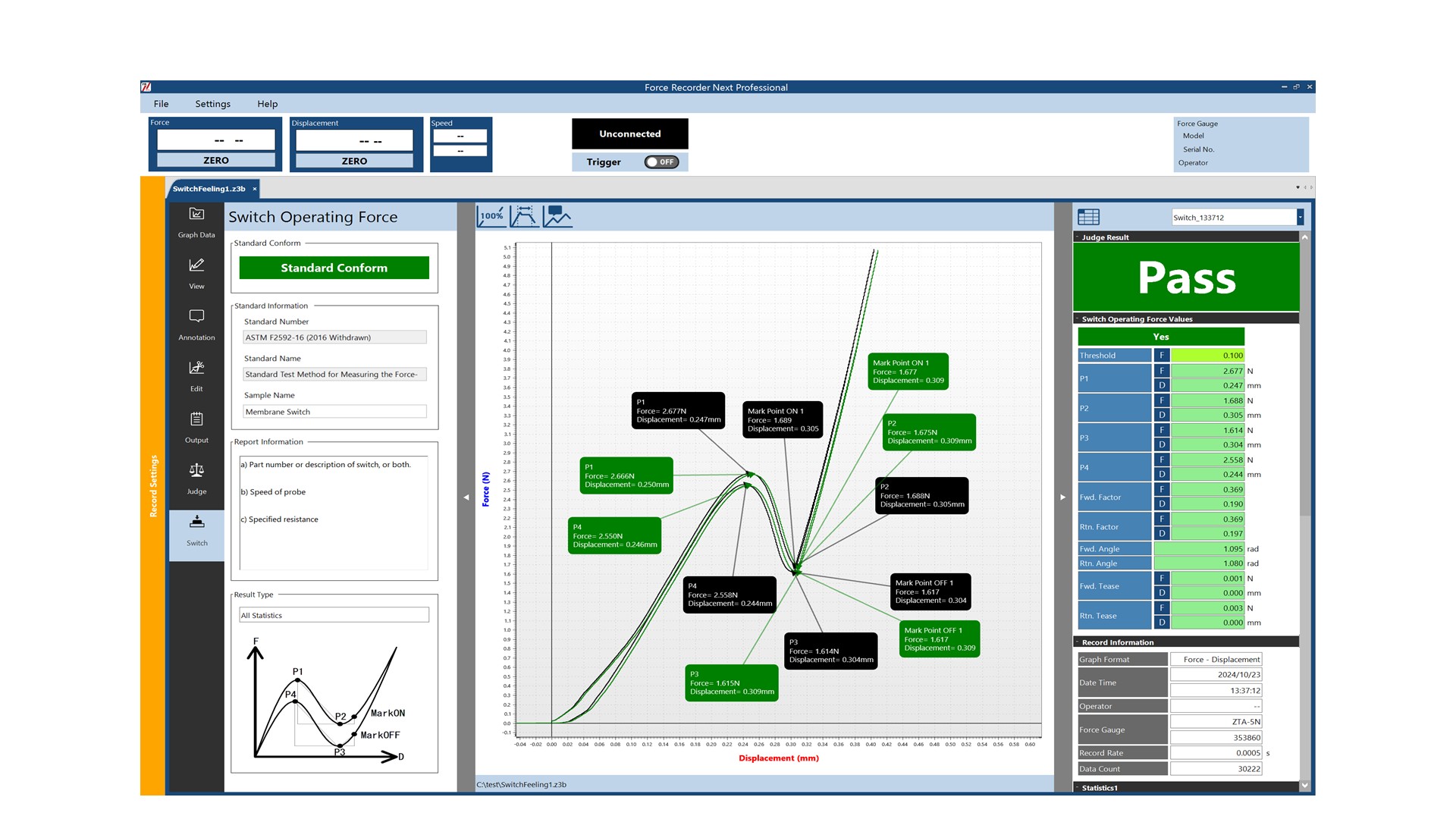
Torque is "the magnitude of force, torsional moment (turning or twisting force) that acts on an object when it rotates". Torque is the result of force multiplied by distance, and is defined as force (F) x distance (L) = torque (N), and the unit of torque is expressed in "N-m (Newton meter)".
The greater the distance to the point of force action, the greater the torque will be for the same amount of force (F). This is the same as the "The Principle of Leverage". For example, when turning a door handle to open a door, the longer the handle, the easier it is to open the door. If the same torque is required, a longer distance (L) from the point of action will result in a smaller force (F).
We perform actions that generate torque on a daily basis, such as opening the lid of a plastic bottle or turning the dial of a car air conditioner. Therefore, on site of product development and quality control of companies, measurement of torque values is commonly used as one indicator to check the usability and safety of products.
Unit of Torque Newton-meter (N-m)
In Japan, the Measurement Act requires that "N-m (Newton-meter)" and "N-cm (Newton-centimeter)" be used as the unit of torque (moment of force). In other countries, the units kgf-m (kilogram-force meter) and lbf-in (pound-inch) are used.
(Example) 1N-m = 100N-cm
1N-m ≒ 0.1kgf-m
1N-m ≒ 8.85lbf-in (1in = 0.254m)
Converter
Convenient Unit/Torque/
Tension conversion
6 Significant Digits (*Significant digits are meaningful digits that do not include zeros, which are used to indicate the scale.)
Products

HERE!
 Attachments, Grips & Fixtures
Attachments, Grips & Fixtures
 Custom Made
Custom Made
 Measurements in Special Environment
Measurements in Special Environment
 Temperature and Angle Adjustable Peel Tester
Temperature and Angle Adjustable Peel Tester
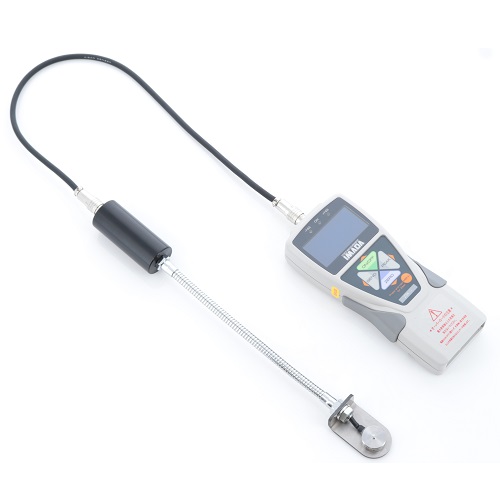 Spot Welding Pressure Gauge
Spot Welding Pressure Gauge
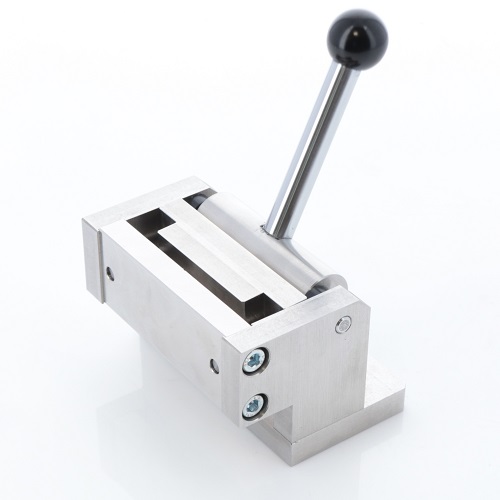 Attachment to Bend Sample 90 Degrees
Attachment to Bend Sample 90 Degrees
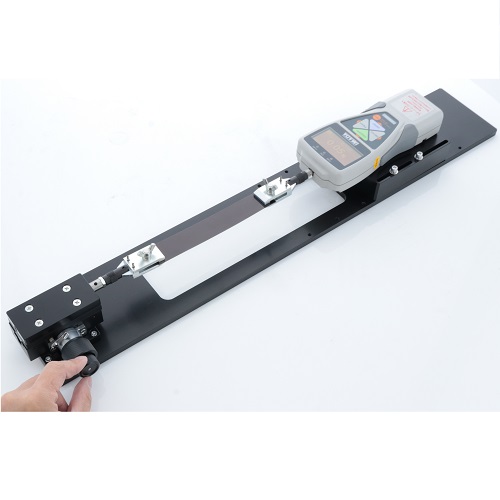 Horizontal Test Stand with Fine Adjustment Knob
Horizontal Test Stand with Fine Adjustment Knob
 Tester With Thermostatic Chamber
Tester With Thermostatic Chamber
 Tester With Far-infrared Heater
Tester With Far-infrared Heater
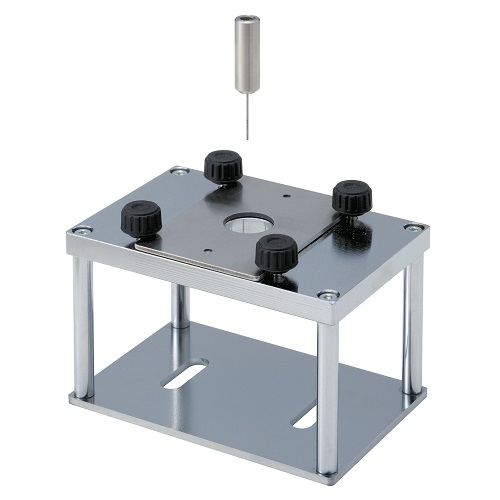
 Table for Compression Load Cell
Table for Compression Load Cell
 Test Stand for Testing at the Desired Position
Test Stand for Testing at the Desired Position
 Particular Samples Measurements
Particular Samples Measurements
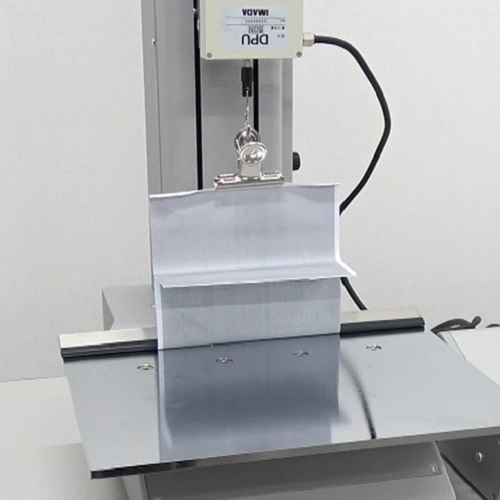 Peel Test Fixture for Crimped Postcard
Peel Test Fixture for Crimped Postcard
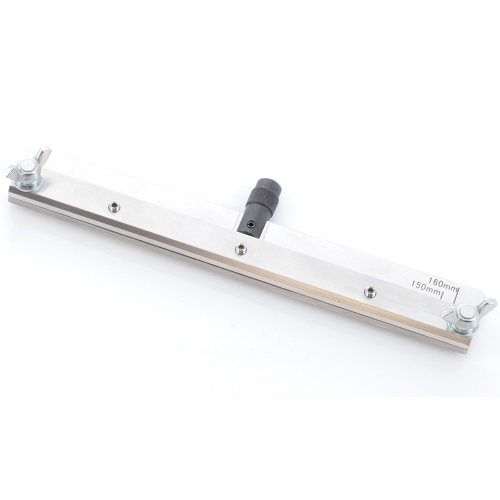 Attachment for Fixing Wide and Thin Materials
Attachment for Fixing Wide and Thin Materials
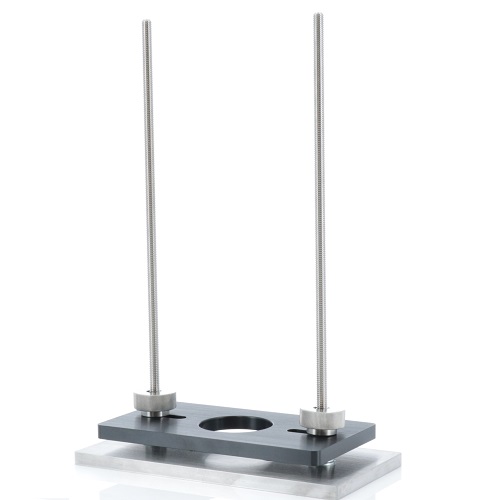 Attachment for Wine Cork Extraction Test
Attachment for Wine Cork Extraction Test
 Attachments for 90 degree score bend test
Attachments for 90 degree score bend test
 Attachments to measure forces to open flat pack carton
Attachments to measure forces to open flat pack carton
 Attachments for break strength testing of lipsticks or lip balms
Attachments for break strength testing of lipsticks or lip balms
 High capacity dual-column motorized test machine for compression test
High capacity dual-column motorized test machine for compression test
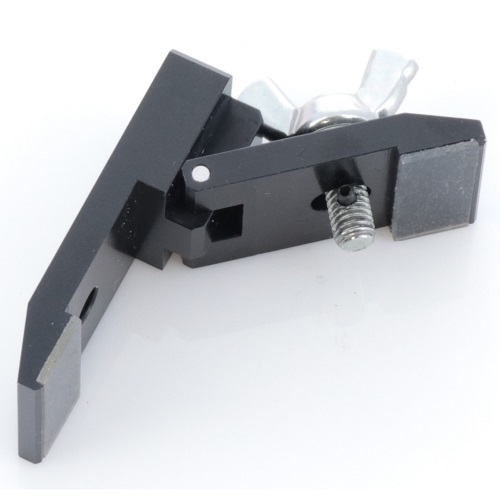 Film Grip with Openable Gripping Part
Film Grip with Openable Gripping Part
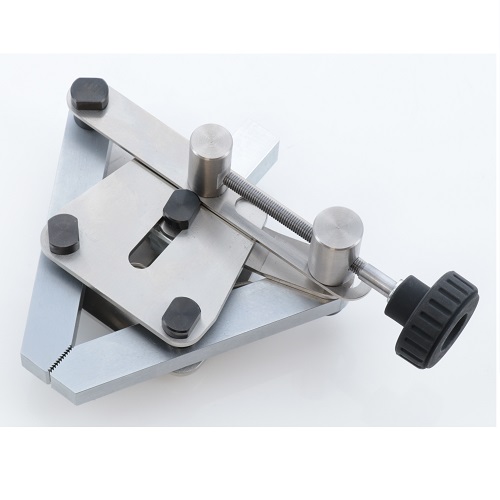 Pantograph Grip with Pressurization Mechanism
Pantograph Grip with Pressurization Mechanism
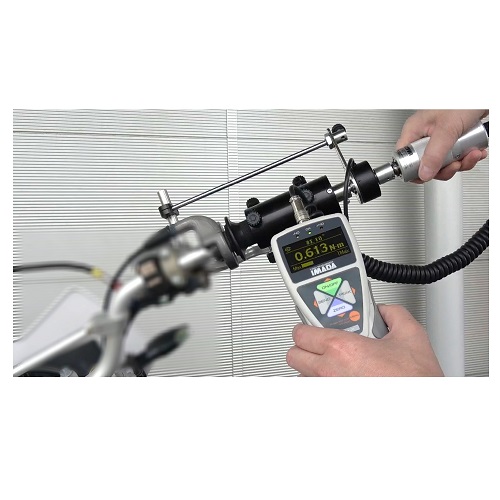 Motorcycle Accelerator Torque Test Fixture
Motorcycle Accelerator Torque Test Fixture
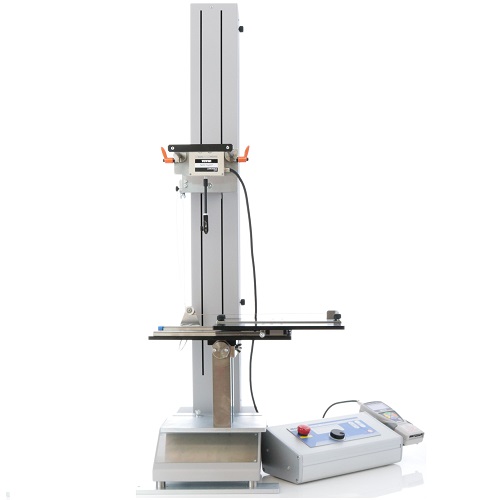 Peel Test Fixture for Solar Cell Ribbon
Peel Test Fixture for Solar Cell Ribbon
 Test Stand With Large Table
Test Stand With Large Table
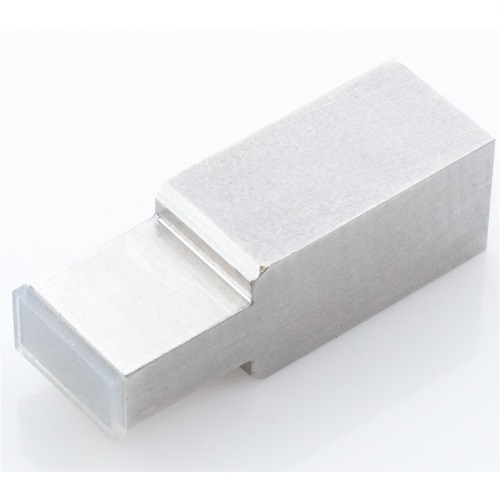 Compression Test Attachment for LCD Panel
Compression Test Attachment for LCD Panel
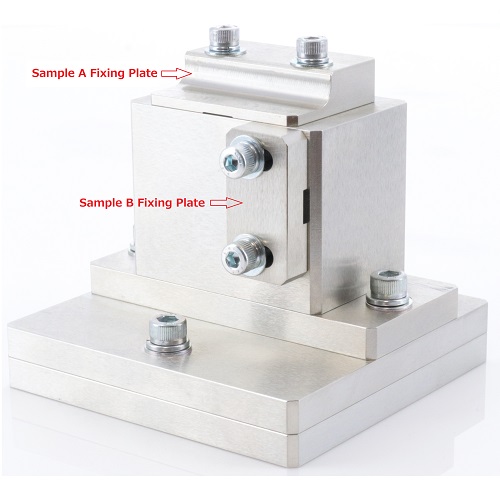 L-shaped Sample Fixture
L-shaped Sample Fixture
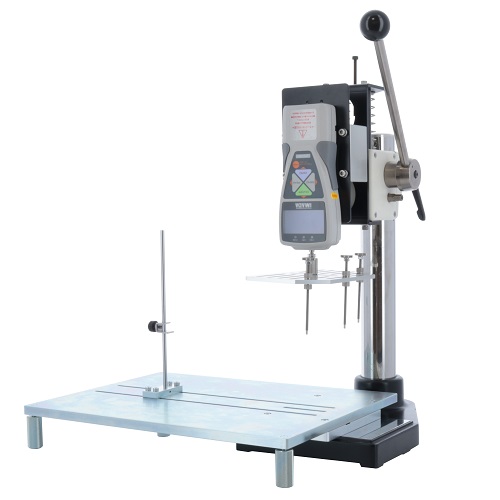 Attachment for Opening/Closing Force Test of Takeout Container Lid
Attachment for Opening/Closing Force Test of Takeout Container Lid
 Attachment for Squeezing Force Test of Eye Drop Bottles
Attachment for Squeezing Force Test of Eye Drop Bottles
 Compression Test Attachment for Squeeze Tube
Compression Test Attachment for Squeeze Tube
 Attachment for Welded Nut Tension Test
Attachment for Welded Nut Tension Test
 Attachment for Tube Tension Strength Test
Attachment for Tube Tension Strength Test
 Attachment for Hard-to-Grip Samples
Attachment for Hard-to-Grip Samples
 Attachment for Compression Test of Nasal Spray
Attachment for Compression Test of Nasal Spray
 Individually Adjustable Torque Chuck Attachment
Individually Adjustable Torque Chuck Attachment
 Resistance Force Measurement jig for Hair Combing Test
Resistance Force Measurement jig for Hair Combing Test
 Attachment for Lateral Compression Test of Cup Containers
Attachment for Lateral Compression Test of Cup Containers
 Water-Proof Shield for Motorized Torque Test Stand
Water-Proof Shield for Motorized Torque Test Stand
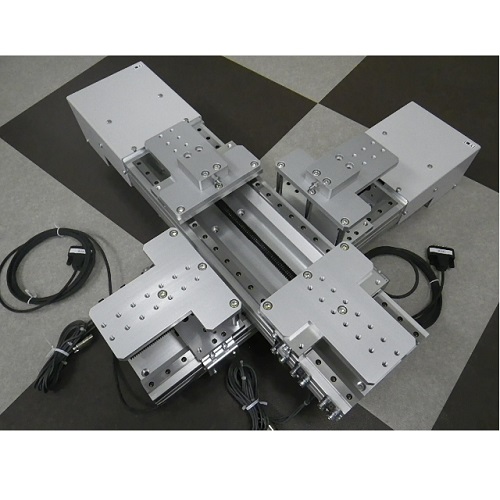 Biaxial Tension Tester
Biaxial Tension Tester
 Resize & Modification
Resize & Modification
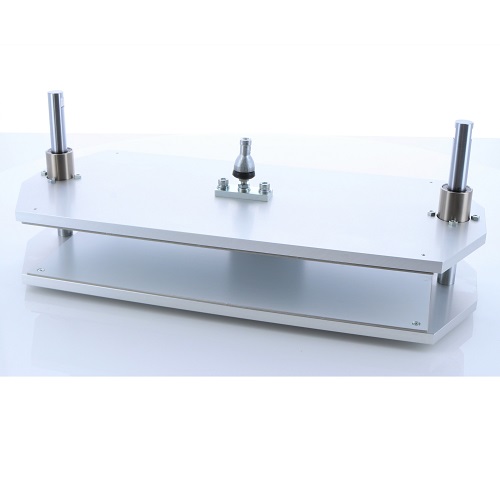 Press Test Fixture (Wide Size)
Press Test Fixture (Wide Size)
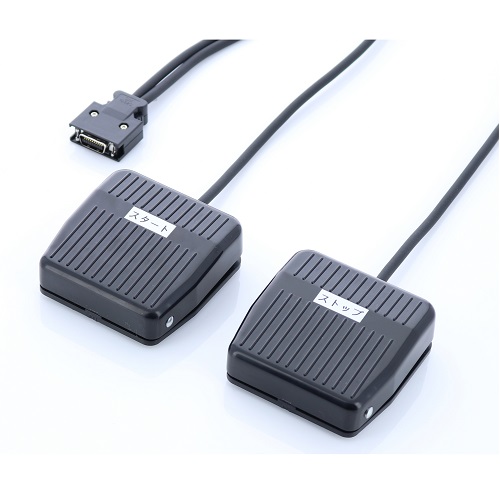 Remote Control Switch for Motorized Test Stand
Remote Control Switch for Motorized Test Stand
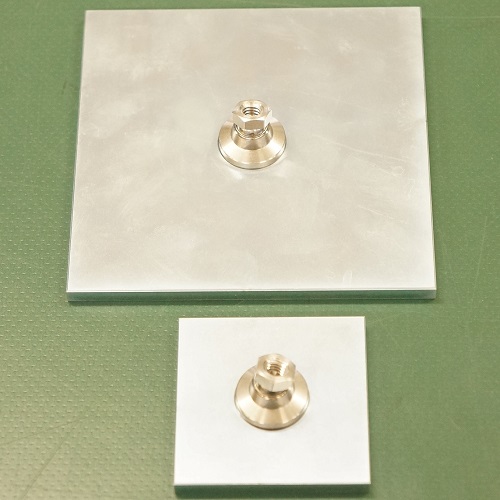 Semi-Customized Compression Attachments
Semi-Customized Compression Attachments
 Large Size of Compression Tester
Large Size of Compression Tester
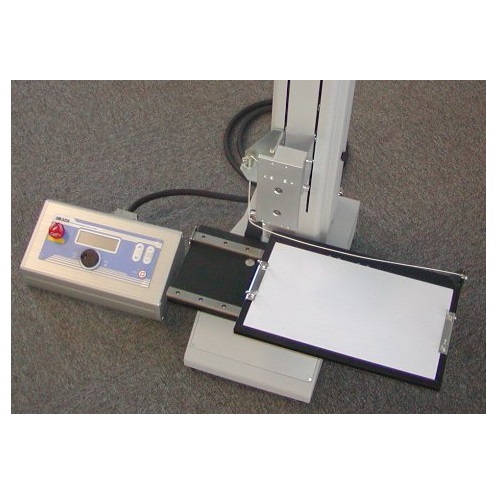 Large Size of 90 Degree Peel Tester
Large Size of 90 Degree Peel Tester
 Force Control Cable with Signal Output Box
Force Control Cable with Signal Output Box
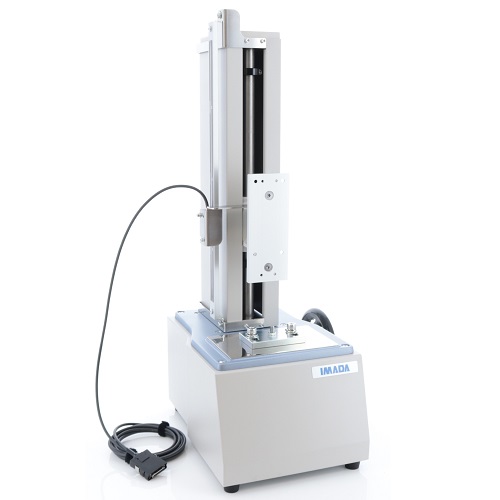 Manual Test Stand with Displacement Output Option
Manual Test Stand with Displacement Output Option
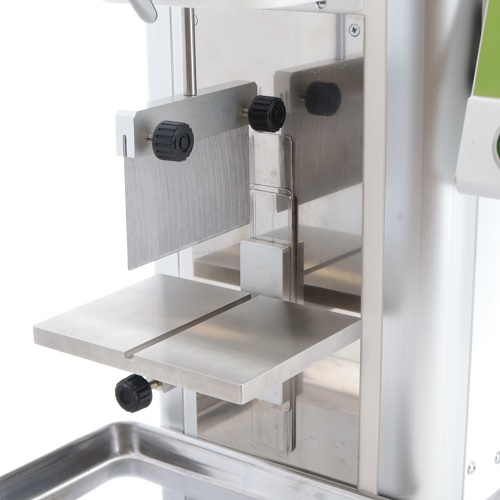 Cutting Base Plate with groove and knife edge probe
Cutting Base Plate with groove and knife edge probe
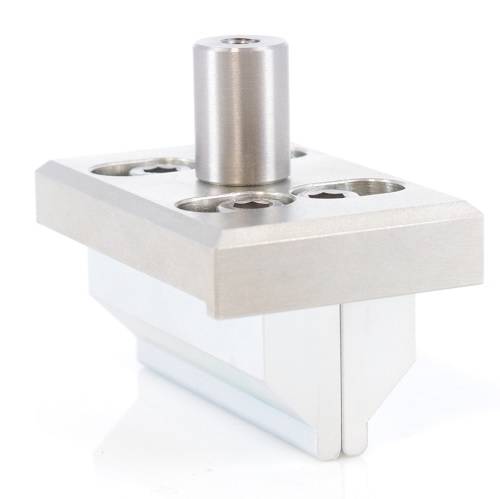 Upper attachment for 4-point bending test
Upper attachment for 4-point bending test
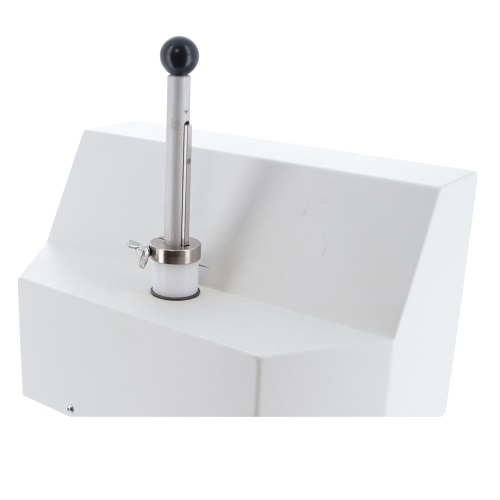 Main shaft stopper with a butterfly screw for MTS series
Main shaft stopper with a butterfly screw for MTS series
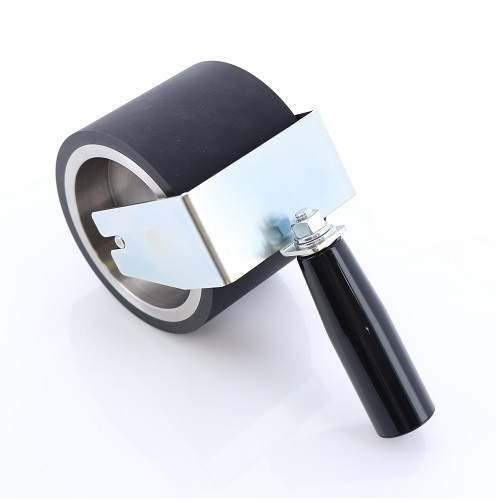 Wide Rubber Roller for Peel Test
Wide Rubber Roller for Peel Test
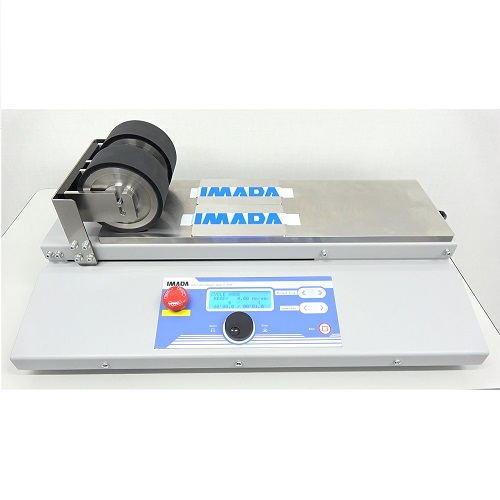 Motorized Rubber Roller for Peel Test
Motorized Rubber Roller for Peel Test
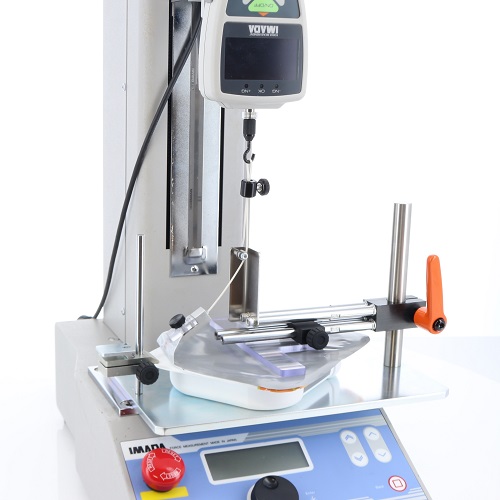 Peel Fixture for Packaged Cooked Rice Lid
Peel Fixture for Packaged Cooked Rice Lid
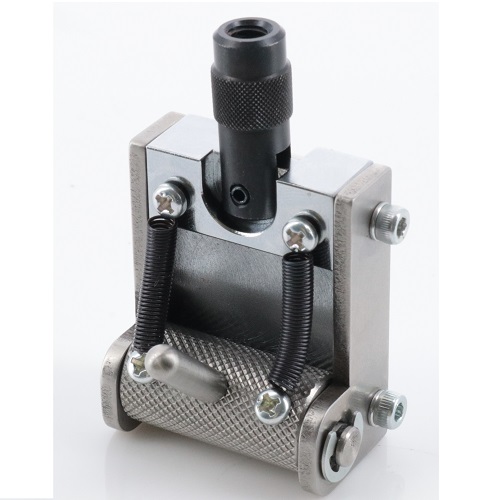 Cam grip with spring
Cam grip with spring
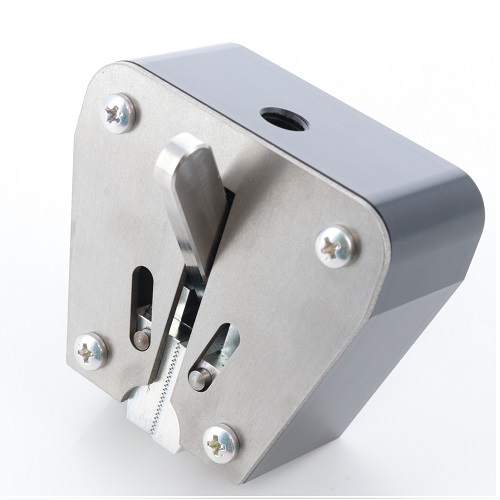 Wedge Grip Without Adaptor
Wedge Grip Without Adaptor
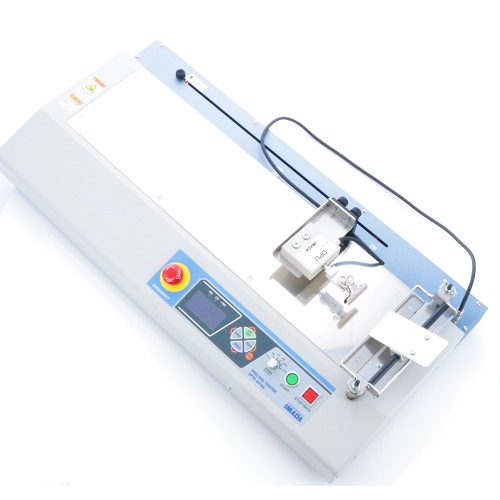 Customized Peeling Tester
Customized Peeling Tester
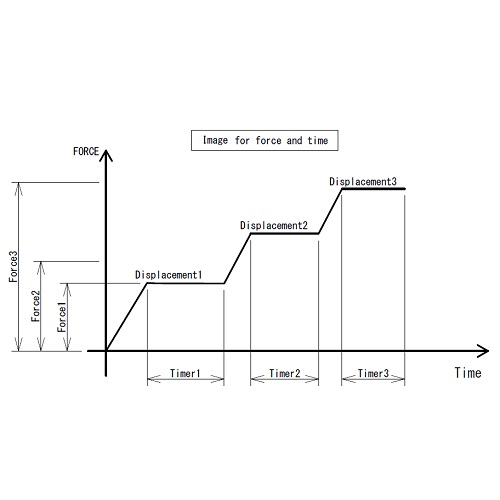
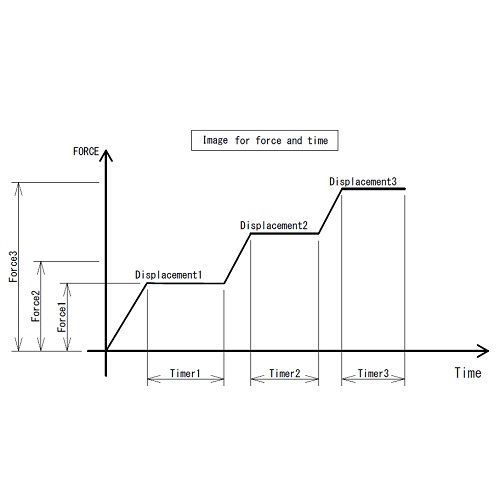 Test Stand with 3-stage Force/Displacement setting/holding function
Test Stand with 3-stage Force/Displacement setting/holding function
 Torque Stand Shaft for Child Proof Lock Measurement
Torque Stand Shaft for Child Proof Lock Measurement
 90 degree Peel Test Jig (High Capacity Type)
90 degree Peel Test Jig (High Capacity Type)
 Tabletop Force Gauge Calibration Unit (High Capacity Type)
Tabletop Force Gauge Calibration Unit (High Capacity Type)
 One-touch toggle clamp for Coefficient of Friction Fixture
One-touch toggle clamp for Coefficient of Friction Fixture
 Compact Motorized Test Stand
Compact Motorized Test Stand
 Tube Fixing Jig
Tube Fixing Jig
 Visualized Film Chuck
Visualized Film Chuck
 Standards-Compliant Measurement
Standards-Compliant Measurement
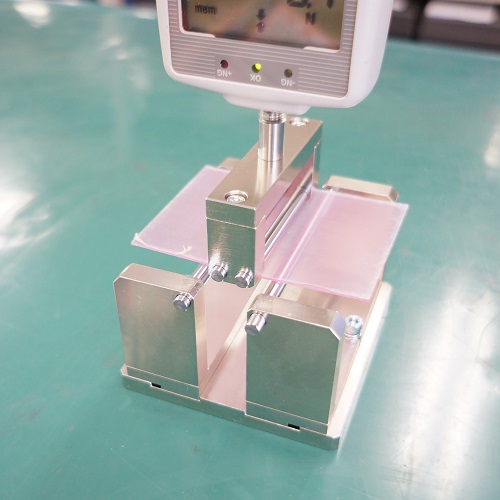 ISO 14704: 2000 Fine Ceramics 4-Point Bend Tester
ISO 14704: 2000 Fine Ceramics 4-Point Bend Tester
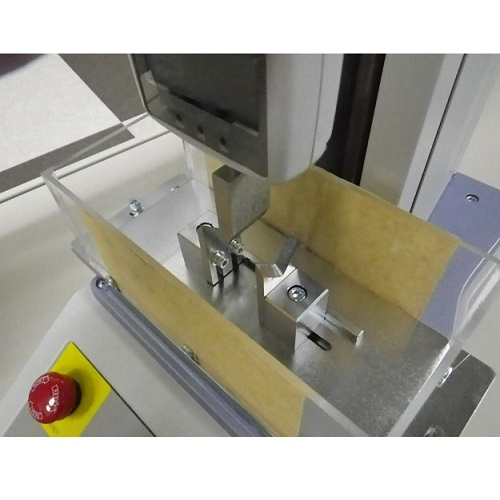 Ampoule 3-Point Bend Tester
Ampoule 3-Point Bend Tester
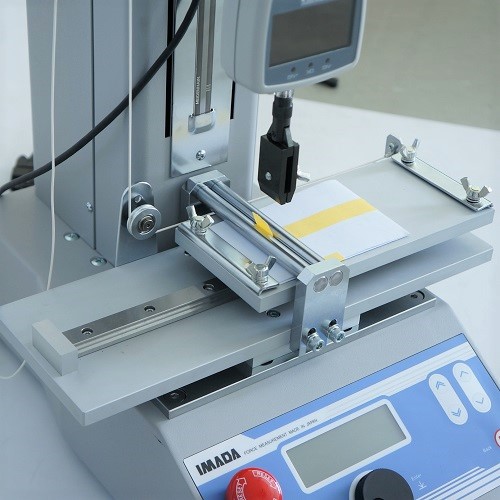 ISO/IEC 10373-1: 2006 Peel Tester of Identification Card
ISO/IEC 10373-1: 2006 Peel Tester of Identification Card
 ISO 17480: 2015 Peel Tester for Gable-Top Package
ISO 17480: 2015 Peel Tester for Gable-Top Package
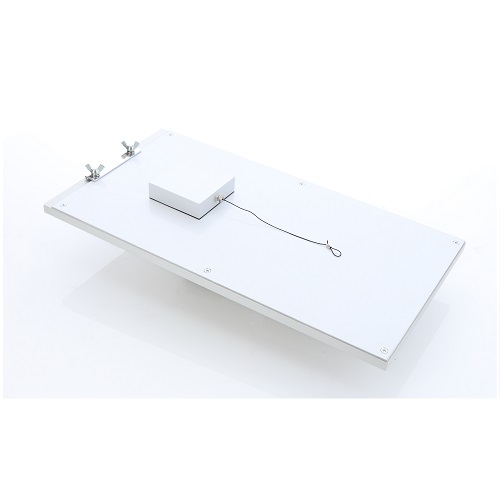 ASTM D1894: 2014 Coefficient of Friction (COF) Tester
ASTM D1894: 2014 Coefficient of Friction (COF) Tester
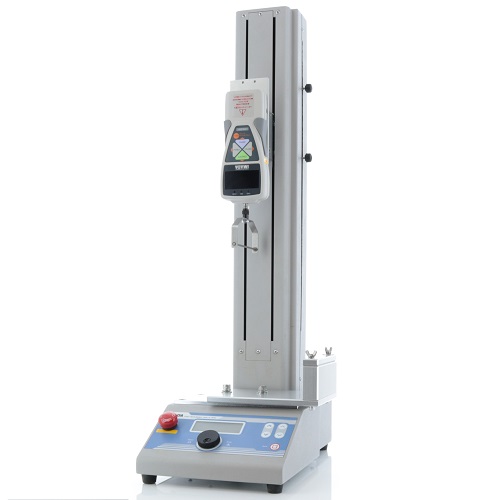 Attachments for score bend test
Attachments for score bend test
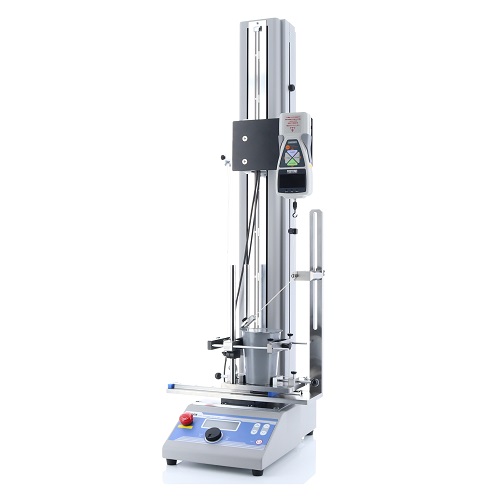 ISO 17480: 2015 45 Degree Complete Peel Test Fixture for Container Lid
ISO 17480: 2015 45 Degree Complete Peel Test Fixture for Container Lid
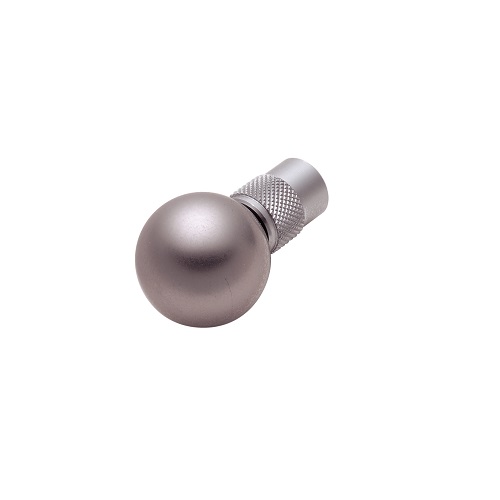
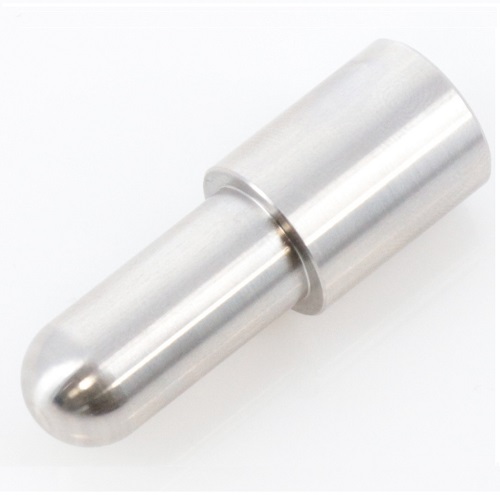 IEC 61010-1 (2010) Spherical Jig for Compression Testing
IEC 61010-1 (2010) Spherical Jig for Compression Testing
 ASTM D4032(Withdrawn 2025)Standard Test Attachment for Fabric Stiffness by Circular Bend Procedure
ASTM D4032(Withdrawn 2025)Standard Test Attachment for Fabric Stiffness by Circular Bend Procedure
 Peel Test Jig for Gable-Topped Package (No sample cut type)
Peel Test Jig for Gable-Topped Package (No sample cut type)